Module 5: Understanding Basics of AI Agents and their Impact on Clinical Practice & Administrative Tasks in Gastroenterology
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a system that perceives its environment, processes data, makes decisions, and takes actions autonomously. It can adapt dynamically to new information and guide its own behavior using Large Language Models (LLMs), decision-making algorithms, and tool integrations.
In this module Part 1- provides the potential clinical and administrative tasks that can be augmented by AI agents. Part 2 of this module will go over the basics of the technology behind AI agents.
Part 1: How can AI agents Help your Clinical Practice?
AI Agents in Gastroenterology: Revenue Cycle Management & Prior Authorization
AI agents can automate and optimize many administrative burdens in gastroenterology practice, including revenue cycle management (RCM) and prior authorization (PA). Below, we explore how AI-driven automation can reduce delays, minimize denials, and improve reimbursement processes.
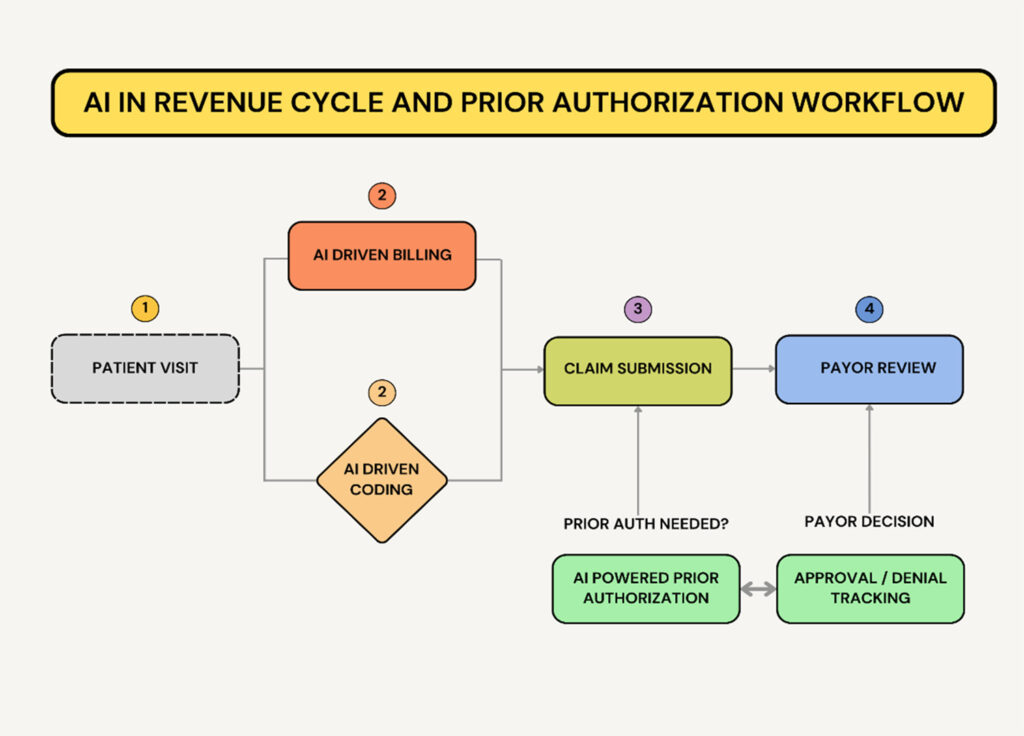
AI Agents in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) involves tracking patient revenue from appointment scheduling to final payment. AI agents can optimize this process by:1. AI for Medical Coding & Billing Optimization
Problem:- Errors in medical coding lead to claim denials and revenue losses.
- Manual coding is time-consuming and prone to mistakes.
- AI-powered coding assistants analyze endoscopy reports and auto-suggest accurate CPT, ICD-10, and HCPCS codes.
- AI audits claims before submission to flag potential denials based on payer rules.
- Predicts reimbursement issues and suggests corrections before claims submission.
- After a colonoscopy, AI scans the procedure report, extracts key details (polyp size, number, and location), and assigns correct CPT and ICD-10 codes for insurance submission.
2. AI for Denial Prediction & Claims Management
Problem:- Insurance denials due to missing information or incorrect documentation delay payments.
- Appeals are labor-intensive and often require physician involvement.
- How AI Helps: AI predicts claim denials based on payer history and suggests corrections before submission. AI automates appeals, pulling relevant EHR documentation, pathology reports, and procedure notes. AI flags underpayments and automatically resubmits claims when payer discrepancies are detected.
- AI detects denial risks for a GERD procedure due to missing documentation of refractory symptoms and alerts the biller to attach previous medication trials.
AI Agents in Prior Authorization (PA)
Prior authorization (PA) is a major bottleneck in gastroenterology, delaying care for procedures like biologic therapy for IBD, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), and FibroScan for liver disease. AI can streamline PA requests, track approvals, and reduce manual work.3. AI for Automated Prior Authorization Submission
Problem:- PA requests require detailed medical necessity documentation, causing delays in biologic therapy approvals.
- Staff spend hours faxing, calling, and re-submitting requests.
- AI extracts clinical data from EHRs, ensuring all required details (e.g., lab results, failed medications, imaging findings) are included.
- AI autofills PA forms and submits directly to payers. AI tracks payer rules in real-time and suggests the correct documentation for each insurer.
- A patient with Crohn’s disease needs ustekinumab. AI pulls previous treatments, colonoscopy findings, and CRP levels and submits a complete PA request in minutes.
4. AI for PA Status Tracking & Follow-Ups
Problem:- Manual PA follow-ups take time.
- Lack of real-time tracking leads to delays in insurance approvals.
- AI tracks authorization status and alerts staff when an appeal is needed.
- AI automates payer follow-ups, reducing administrative workload.
- AI notifies clinicians when PA is approved, ensuring timely patient care.
- AI detects an insurer delay for a FibroScan approval and auto-escalates the request, ensuring faster patient access.
AI Agents in Gastroenterology: Revenue Cycle Management & Prior Authorization
AI agents can automate and optimize many administrative burdens in gastroenterology practice, including revenue cycle management (RCM) and prior authorization (PA). Below, we explore how AI-driven automation can reduce delays, minimize denials, and improve reimbursement processes.AI Agents in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) involves tracking patient revenue from appointment scheduling to final payment. AI agents can optimize this process by:1. AI for Medical Coding & Billing Optimization
Problem:- Errors in medical coding lead to claim denials and revenue losses.
- Manual coding is time-consuming and prone to mistakes.
- AI-powered coding assistants analyze endoscopy reports and auto-suggest accurate CPT, ICD-10, and HCPCS codes.
- AI audits claims before submission to flag potential denials based on payer rules.
- Predicts reimbursement issues and suggests corrections before claims submission.
- After a colonoscopy, AI scans the procedure report, extracts key details (polyp size, number, and location), and assigns correct CPT and ICD-10 codes for insurance submission.
2. AI for Denial Prediction & Claims Management
Problem:- Insurance denials due to missing information or incorrect documentation delay payments.
- Appeals are labor-intensive and often require physician involvement.
- AI predicts claim denials based on payer history and suggests corrections before submission.
- AI automates appeals, pulling relevant EHR documentation, pathology reports, and procedure notes.
- AI flags underpayments and automatically resubmits claims when payer discrepancies are detected.
- AI detects denial risks for a GERD procedure due to missing documentation of refractory symptoms and alerts the biller to attach previous medication trials.
AI Agents in Prior Authorization (PA)
Prior authorization (PA) is a major bottleneck in gastroenterology, delaying care for procedures like biologic therapy for IBD, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), and FibroScan for liver disease. AI can streamline PA requests, track approvals, and reduce manual work.3. AI for Automated Prior Authorization Submission
Problem:- PA requests require detailed medical necessity documentation, causing delays in biologic therapy approvals.
- Staff spend hours faxing, calling, and re-submitting requests.
- AI extracts clinical data from EHRs, ensuring all required details (e.g., lab results, failed medications, imaging findings) are included.
- AI autofills PA forms and submits directly to payers.
- AI tracks payer rules in real-time and suggests the correct documentation for each insurer.
- A patient with Crohn’s disease needs ustekinumab. AI pulls previous treatments, colonoscopy findings, and CRP levels and submits a complete PA request in minutes.
4. AI for PA Status Tracking & Follow-Ups
Problem:- Manual PA follow-ups take time.
- Lack of real-time tracking leads to delays in insurance approvals.
- AI tracks authorization status and alerts staff when an appeal is needed.
- AI automates payer follow-ups, reducing administrative workload.
- AI notifies clinicians when PA is approved, ensuring timely patient care.
- AI detects an insurer delay for a FibroScan approval and auto-escalates the request, ensuring faster patient access.
Part 2: AI agents: Basics for Gastroenterologists:
Now what does an AI agent mean and how do they differ from traditional AI systems?How AI Agents Differ from Traditional Workflows
| Aspect | Traditional Workflow (Rule-Based AI) | AI Agents (Adaptive Systems) |
| Decision-making | Predefined rules & static decision trees | Adapts dynamically based on real-time data |
| Flexibility | Limited – follows fixed paths | Can change strategies based on new inputs |
| Example in GI | Endoscopy software with rigid criteria for polyp classification | AI-assisted colonoscopy that adapts polyp detection based on evolving risk factors |
| Human Oversight | High – requires direct control at each step | Can operate independently but with periodic review |
- A workflow-based system in GI might automatically populate an EHR template after an endoscopy.
- An AI agent, however, can interpret findings, suggest personalized follow-ups, and even adjust recommendations based on the latest research.
Technical Breakdown: How AI Agents Work in Gastroenterology
Core Components of an AI Agent1. Perception Layer (Data Input & Processing)
AI collects input from:- Endoscopy images
- EHRs (Electronic Health Records)
- Patient-reported symptoms
Reasoning Layer (Decision-Making & Predictions)
- AI applies machine learning (ML), transformers (LLMs), and deep learning to analyze the data.
- Example: AI assesses lesion morphology to predict malignancy risk.
2. Action Layer (Decision Execution)
- AI outputs recommendations such as:
- “Recommend biopsy based on AI analysis of lesion irregularity.”
- “Surveillance colonoscopy in 3 years based on polyp size and patient history.”
- Human validation ensures safety & reliability.
3. Feedback & Learning Layer (Continuous Improvement)
- AI updates its knowledge based on new clinical data & clinician feedback.
- Example: AI refines its Barrett’s esophagus progression risk model as more patient data is analyzed.
Practical Applications of AI Agents in Gastroenterology
AI Agents in GI Practice| Application | How AI Agents Improve It | Clinical Benefit |
| Clinical Decision Support | AI reviews symptoms, labs, & EHRs to suggest diagnoses & management | Can enhances diagnostic accuracy |
| Personalized Screening Schedules | AI predicts patient risk for CRC & adjusts follow-up intervals | Can improve guideline adherence |
| Patient Interaction AI (Chatbots) | AI explains conditions, diet recommendations & post-procedure care | Can enhance patient education & adherence |
Future of AI Agents in Gastroenterology
Emerging Capabilities1. Self-Learning AI for GI Risk Stratification
- AI will analyze long-term patient data to predict IBD progression.
2. AI-Augmented Endoscopy Techniques
- Future AI agents could adjust scope movements autonomously to improve visualization.
3. Real-Time Multi-Modal AI Integration
- AI agents will combine data from imaging, lab reports, and patient symptoms to provide comprehensive insights.
Conclusion & Next Steps
- AI agents go beyond rule-based automation—they adapt, learn, and improve decision-making dynamically.
- Gastroenterologists must understand how AI makes decisions to ensure safe, effective implementation.
- Join the AI Workshop at DDW 2025 May 2 noon – 515pm for a hands-on learning of AI-powered GI tools.
Introduction to AI Educational Series
- Module 1: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence for Gastroenterologists
- Module 2: Basics of Machine Learning
- Module 3: Data — The Heart of AI in Medicine
- Module 4: Introduction to Large Language Models (LLMs) for Gastroenterologists
- Module 5:
Understanding Basics of AI Agents and their Impact on Clinical Practice & Administrative Tasks in Gastroenterology
